Tumors can grow on rabbits just as on other mammals. If you want to know more about tumors in rabbits, or if you are suspecting that your rabbit may have a tumor, keep reading this article to find out more about this topic.
Difference Between Tumor And Cancer
It is important to differentiate a tumor from cancer so the rest of the article is more clear. A tumor is a growth that can occur in different parts of the body. It can be benign or malignant. Benign tumors don’t spread to the other parts of the body and they grow more slowly, so they are less dangerous.
Malignant tumors are cancerous, which means that their progression is faster and they can spread to other parts of the body, also known as metastasis. Cancer can happen with or without a growth called a tumor, while a tumor always implies growth.
In this article, we will be talking about both benign and malignant tumors.
Rabbit Tumors
Rabbits can have tumors just as humans can. It is not a pleasant condition for the bunny or the rabbit owner, but it’s crucial to notice that not all tumors are fatal.
Many of them can be surgically removed by a veterinarian and the bunny can continue its life happily and live to see many more good years. Here are some of the possible tumors a bunny can have.
Uterine Tumor In Rabbits
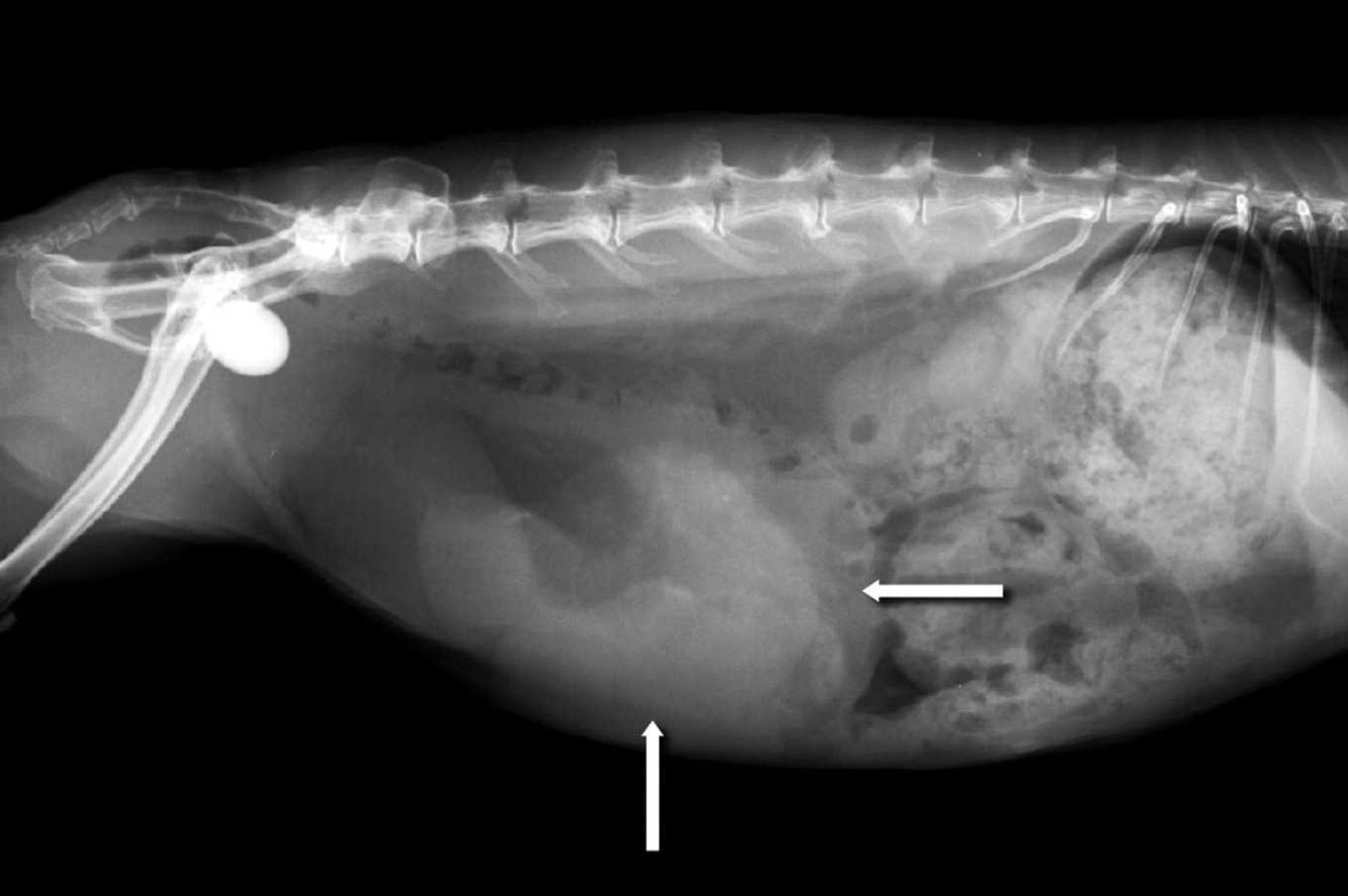
A uterine tumor is a growth that happens in a rabbit’s uterus. It is the most common tumor that can occur in female bunnies and it can be both benign and malignant. Unfortunately, it is usually the latter, so timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial.
Causes And Symptoms
The cause of uterine tumors in rabbits is not entirely clear. Some of the risk factors are endometriosis, a disease in which uterine cells grow on other parts of the reproductive system, and age – the older the rabbit is the bigger risk for this tumor becomes.
Many symptoms can tell you that your rabbit may have a uterine tumor. One of the most indicative ones is bloody vaginal discharge. Other symptoms are changes in behavior – your rabbit can become irritable, sad, and inactive, and your pet may decline food and water.
If the tumor has progressed, you can feel it when you touch your bunny’s stomach. If you notice any of these, it is time to book an appointment with a vet.
Treatment
The treatment for uterine tumors is straightforward – your bunny will probably need surgery. Chemotherapy rarely helps, especially if the tumor has progressed a lot. The prognosis depends on the bunny’s health, age, size of the tumor, and if it has metastasized or not. Overall, more than 80% of rabbits fully recover after the surgery.
The best treatment is prevention. All of the pain and discomfort can be avoided if you neuter your female bunny. If there is no uterus, there is no uterine tumor!
Testicular Tumor In Rabbits
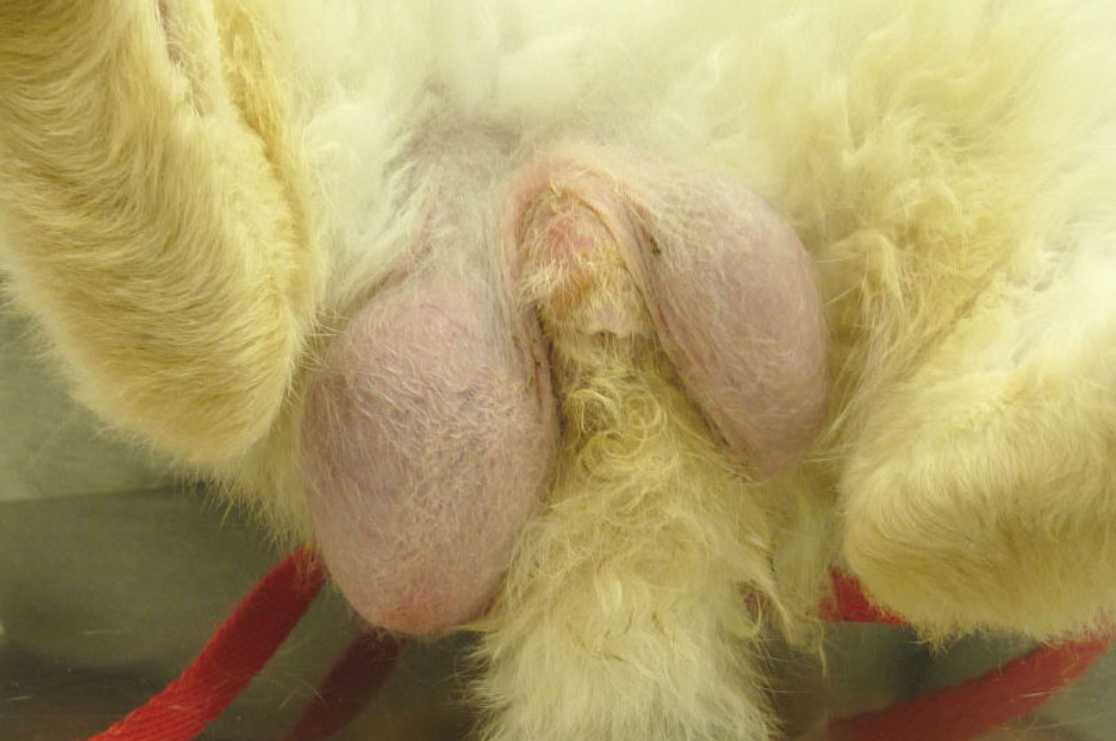
A testicular tumor can happen in rabbits that are not neutered. It is not very common, luckily, and it is almost non-existent in young rabbits. However, if it happens, it can cause great discomfort for your rabbit.
Causes And Symptoms
Like in a uterine tumor, the causes of testicular tumor are not clear; this type of tumor is not studied a lot because it doesn’t happen often. However, symptoms are pretty distinct – a rabbit with a testicular tumor has a growth on one or both testicles.
The enlarged part is firm to touch and easily visible. If the tumor is cancerous, it may spread to other organs, such as the lungs. In this case, a sick rabbit can show signs that resemble those of respiratory infections – troubled breathing, coughing, sneezing, and wheezing.
Treatment
Testicular tumor in rabbits is removed through surgery. The castration is necessary to remove the growth and prevent it from becoming cancerous.
If the tumor has metastasized, the chances of a rabbit recovering become much lower. A vet can still try to save the rabbit with surgery and chemotherapy, but sometimes, euthanasia remains the only option.
Breast Tumor In Rabbits
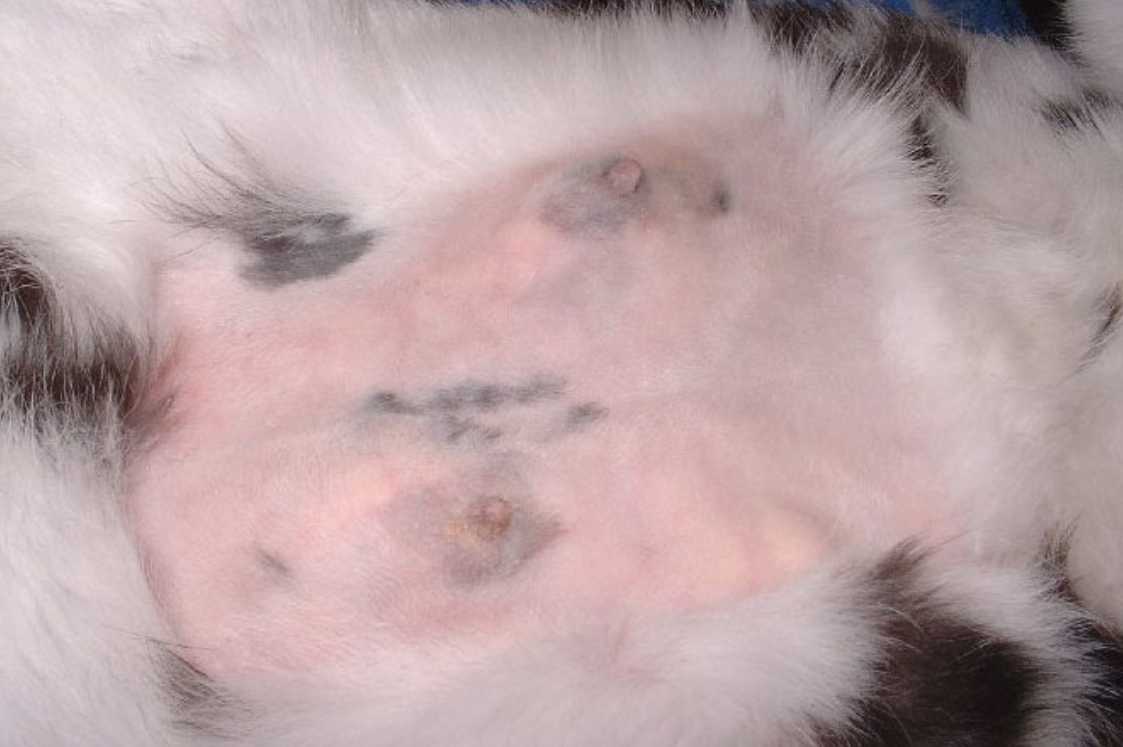
A breast tumor, or mammary tumor, is a type of growth that happens on rabbits’ mammary glands. It is not as common as a uterine tumor, but it has been becoming more and more frequent in the past few decades. It mostly happens in female rabbits; although highly unlikely, a male rabbit can have it too.
Causes And Symptoms
The causes of mammary tumors in rabbits are not completely clear. Studies have shown that early removal of ovaries in rabbits significantly decreases the chances of mammary tumor later in life, which is a good enough reason to neuter your bunny as soon as safe and possible.
Symptoms include the enlargement of mammary glands, secretion from mammary glands, and hair loss around the nipples. If benign, the mammary tumor doesn’t cause the rabbit any pain.
However, if the tumor is cancerous and starts metastasizing, you may notice some behavioral changes in a bunny – lethargy, food and water denial, and overall irritability because of the pain.
Treatment
Treatment for breast tumors in rabbits is surgery, namely mastectomy, which implies the removal of mammary glands.
The predictions of the surgery outcome are not entirely clear, but if a tumor is non-cancerous and the bunny is in good health, there usually isn’t much to worry about. Your pet can wake up from anesthesia as healthy as new and live a long, happy life.
Shope Papilloma Virus Tumors In Rabbits
Shope Papillomavirus is a virus that can cause tumors in different parts of a bunny’s body. This virus can affect both wild and domestic rabbits, and it is usually transmitted by insects, such as mosquitoes and ticks.
Causes And Symptoms
The cause of this kind of tumor is Shope Papilloma Virus. The tumor can grow on any part of a rabbit’s body, but most commonly in the upper part – shoulders, head, and face.
If your rabbit is infected, you can see small, red, and usually, round growths that can progress and become bigger over time. If the tumor turns malignant, it can metastasize to other parts of the body, such as the skin, and cause great discomfort and pain to your pet.
Treatment
Tumors caused by the Shope Papillomavirus can go away within up to six months without any special treatment. In around 25% of the cases, these tumors can become cancerous. In this case, it is necessary to perform surgery as soon as possible to remove the cancer.
If you notice any lesions or growths on your rabbit’s body, you should consult a medical professional right away. They will tell you all you need to know about the care and possible future interventions.
The tumors are not something you should take care of by yourself because only a biopsy can show if the tumor is benign or malignant.
Bone Tumor
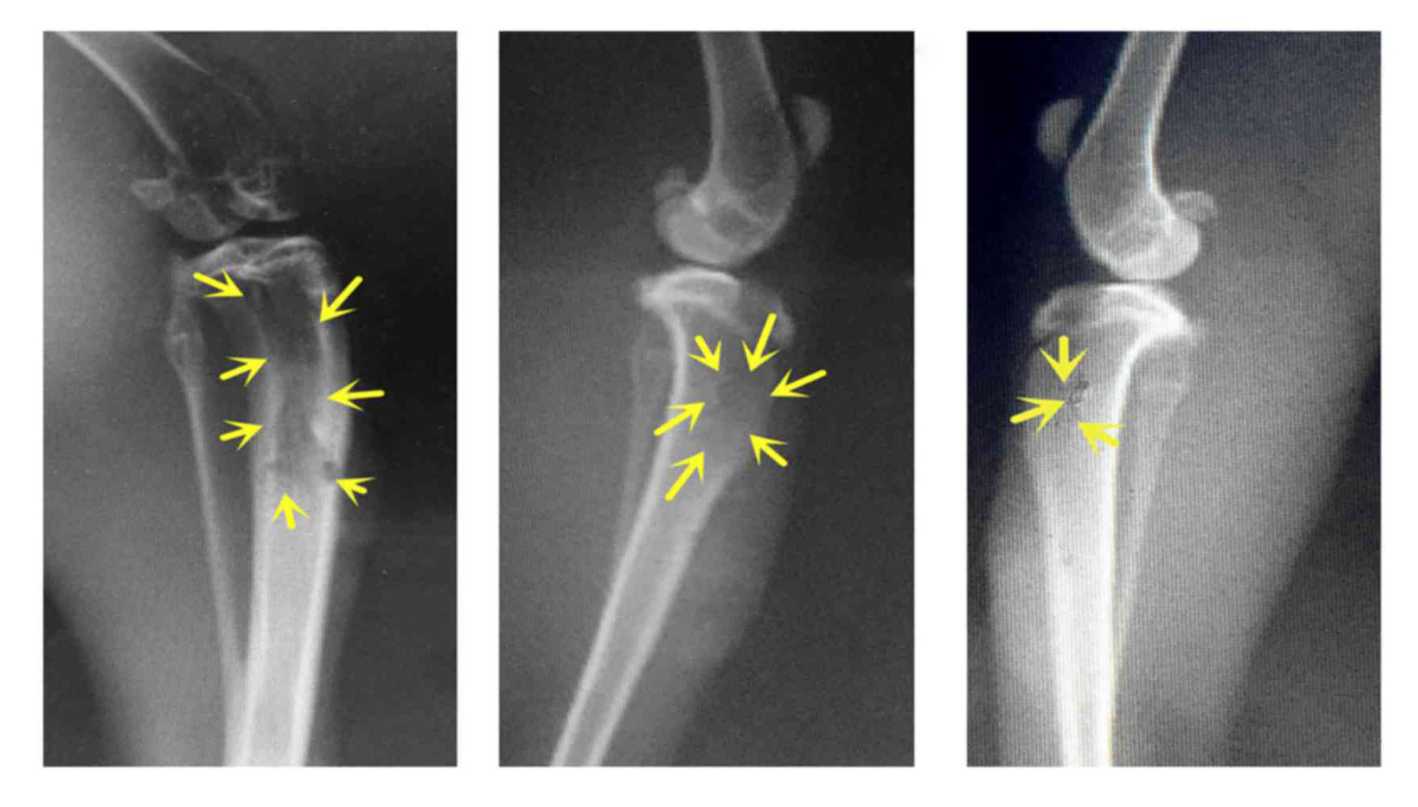
This type of tumor is rare in rabbits, but if it happens, it usually doesn’t come with a good prognosis. Bone tumors are almost always cancerous and another name for them is osteosarcoma.
Causes And Symptoms
It is not understood what exactly causes bone cancer in rabbits. This disease can exist for a long time without any symptoms, making a prompt diagnosis and treatment more difficult.
Some symptoms that can appear are brittle bones, a sudden bone fracture, swelling in the limbs, and behavioral changes that are usually caused by severe pain, such as lethargy and lack of appetite.
Treatment
Treatment for osteosarcoma is the same as for other tumors in rabbits – surgery. Performing surgery is possible if cancer has not metastasized and if it is localized. In some cases, a vet may decide to remove a limb if only one of them is affected.
If cancer has metastasized, the only thing that a vet can do is offer pain meds to help your bunny as much as possible or perform euthanasia. Since the causes of osteosarcoma are not clear, there is not much a bunny owner can do to prevent it. The good thing is that this type of cancer is not common in rabbits.
Are Tumors Common In Rabbits?
The frequency of tumors in rabbits depends on the type of tumor. Testicular and bone tumors are not very common at all; in fact, many veterinarians will tell you that they’ve never had bunny patients with these diseases.
However, uterine and mammary tumors are a bit more frequent, mostly in female rabbits. The good thing is that if you neuter your bunny, the uterine tumor can be completely prevented, and the chances of mammary tumor greatly decreased.
If you notice symptoms of any of these tumors in your rabbit, don’t panic. Chances are something else is happening, so don’t rush to any conclusions without consulting a veterinarian first.
How Long Can A Rabbit Live With Tumor?
Rabbits with tumors can live a long and happy life with prompt and proper treatment – the earlier detection, the better chance of complete recovery. Tumors that become malignant are more difficult to treat, especially if they spread to other parts of the body. However, even in this case, a bunny can have a chance of surviving and recovering.
Summary
Rabbits can grow different types of tumors in different parts of their lives. Some tumors, such as uterine and mammary, are more common. Others, such as testicular and osteosarcoma are very rare. Prevention usually implies neutering your rabbit early.
The prognosis of a diagnosed tumor depends on the type of tumor, progression, and possible malignancy and metastasis.
Disclaimer: Use this article for unofficial information only. This article is not a substitute for medical advice and cannot be used as such. Always consult a veterinarian on any dilemmas or suspicions that you may have about your rabbit’s health.